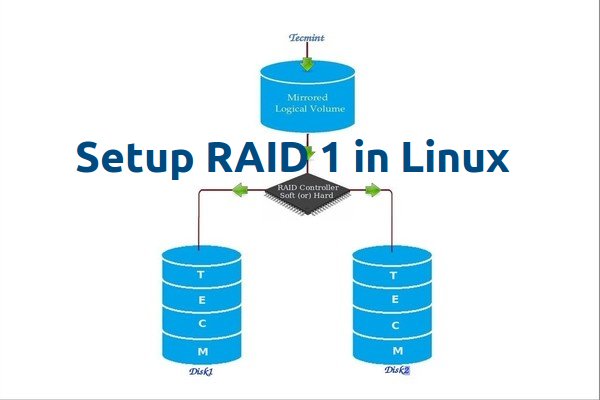
RAID Mirroring means an exact clone (or mirror) of the same data writing to two drives. A minimum two number of disks are more required in an array to create RAID1 and it’s useful only, when read performance or reliability is more precise than the data storage capacity.
Mirrors are created to protect against data loss due to disk failure. Each disk in a mirror involves an exact copy of the data. When one disk fails, the same data can be retrieved from other functioning disk. However, the failed drive can be replaced from the running computer without any user interruption.
Features of RAID 1
- Mirror has Good Performance.
- 50% of space will be lost. Means if we have two disk with 500GB size total, it will be 1TB but in Mirroring it will only show us 500GB.
- No data loss in Mirroring if one disk fails, because we have the same content in both disks.
- Reading will be good than writing data to drive.
Requirements
Minimum Two number of disks are allowed to create RAID 1, but you can add more disks by using twice as 2, 4, 6, 8. To add more disks, your system must have a RAID physical adapter (hardware card).
Here we’re using software raid not a Hardware raid, if your system has an inbuilt physical hardware raid card you can access it from it’s utility UI or using Ctrl+I key.
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
► Read more: http://adf.ly/1n41as
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
No comments:
Post a Comment