The timedatectl command is a new utility for RHEL/CentOS 7 and Fedora 21+ based distributions, which comes as a part of systemd system and service manager, a replacement for old traditional date command used in sysvinit daemon based Linux distributions.
In this tutorial, am going to take you through the ways you can manage time on your Linux system by setting the date, time, timezone and synchronize time with NTP from the terminal using new timedatectl command.
It is always a good practice to maintain the correct time on your Linux server or system and it can have the following advantages:
- maintain a timely operation of system tasks since most tasks in Linux are controlled by time.
- correct time for logging events and other information on the system and many more.
How to Find and Set Local Timezone in Linux
1. To display the current time and date on your system, use the timedatectl command from the commandline as follows:
In the scrrentcast above, RTC time: is the hardware clock time.
2. The time on your Linux system is always managed through the timezone set on the system, to view your current timezone, do it as follows:
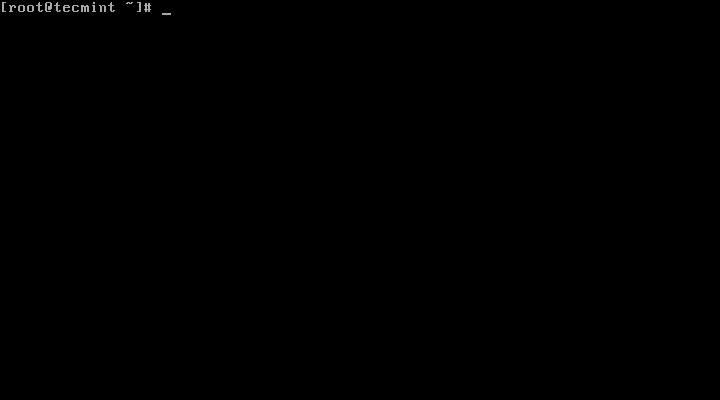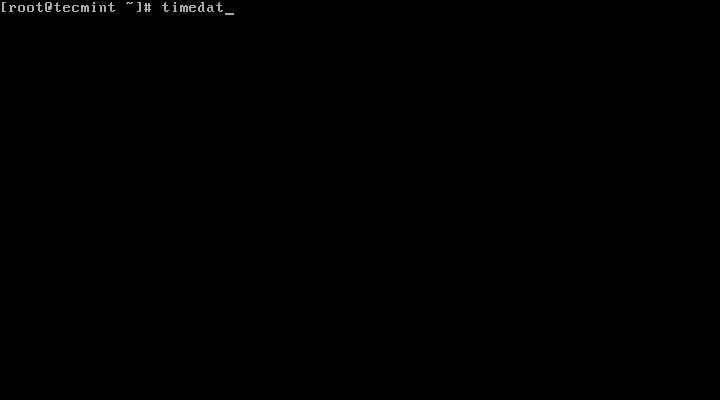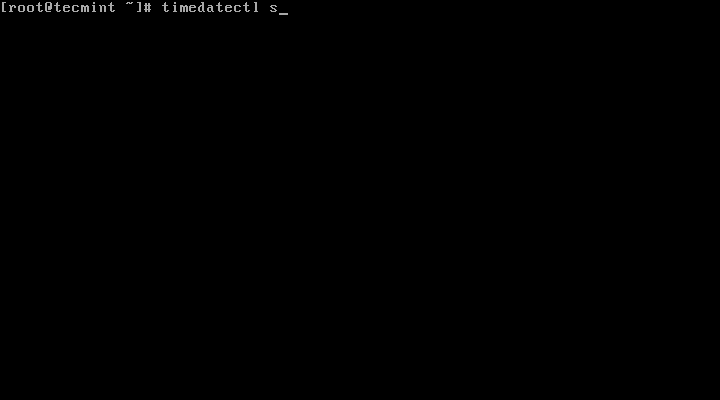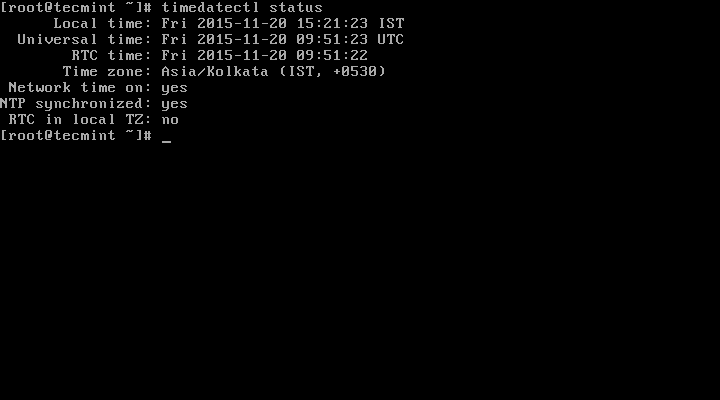
No comments:
Post a Comment