System Administration involves many activities one of which is monitoring and checking for how long your Linux system has been running. It is always a good idea to keep track of system uptime in order to optimize the use of system resources.
In this guide, we shall look at a Linux tool called tuptime that can help System Administrators to know for how long a Linux machine has been up and running.
What is tuptime?
tuptime is a tool used for reporting the historical and statistical running time (uptime) of a Linux system, which keeps it between restarts. This tool works more less like the uptime command but though it provides a more advanced output.
This command line tool can:
- Register used kernels.
- Register the first boot time.
- Count system startups.
- Count good and bad shutdowns.
- Calculate uptime and downtime percentage since first boot time.
- Calculate the largest, shortest and average uptime and downtime.
- Calculate the accumulated system uptime, downtime and total.
- Print current uptime.
- Print formatted table or list with most of the previous values stored.
Requirements
- Linux or FreeBSD OS.
- Python 2.7 or 3.x installed but latest version is recommended.
- Python modules (sys, os, optparse, sqlite3, datetime, locale, platform, subprocess, time).
How to Install tuptime in Linux
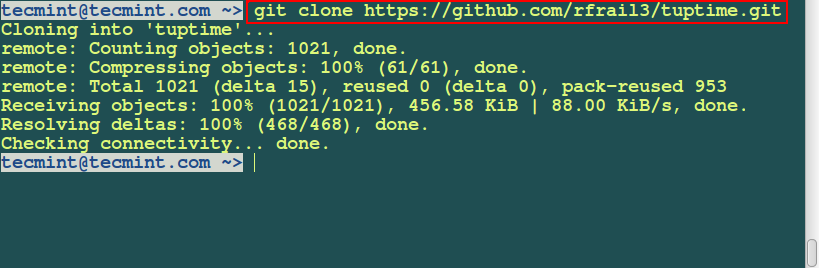
First you need to clone the repository by running the command below:
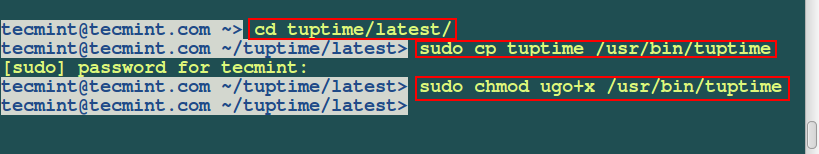
Then move into the latest directory inside the tuptime directory. Next, copy tuptime script inside the latestdirectory to /usr/bin and set executable permission as shown.
Now, copy the cron file tuptime/latest/cron.d/tuptime to /etc/cron.d/tuptime and set executable permission as follows.
No comments:
Post a Comment