When you run a command, it produces some kind of output: either the result of a program is suppose to produce or status/error messages of the program execution details. Sometimes, you may want to store the output of a command in a variable to be used in a later operation.
In this post, we will review the different ways of assigning the output of a shell command to a variable, specifically useful for shell scripting purpose.
To store the output of a command in a variable, you can use the shell command substitution feature in the forms below:
Below are a few examples of using command substitution.
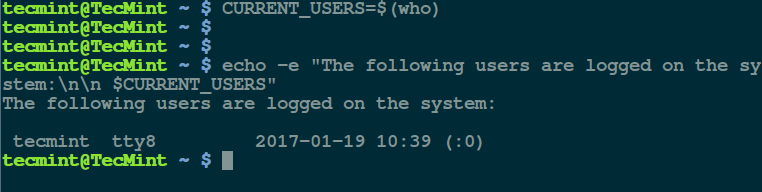
In this first example, we will store the value of
who (which shows who is logged on the system) command in the variable CURRENT_USERS user:
Then we can use the variable in a sentence displayed using the echo command like so:
In the command above: the flag
-e means interpret any escape sequences ( such as \n for newline) used. To avoid wasting time as well as memory, simply perform the command substitution within the echo command as follows:
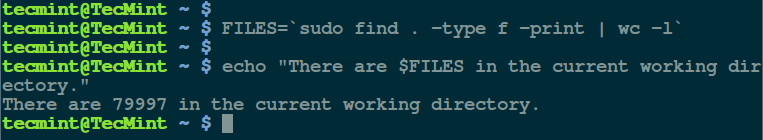
Next, to demonstrate the concept using the second form; we can store the total number of files in the current working directory in a variable called
FILES and echo it later as follows:
That’s it for now, in this article, we explained the methods of assigning the output of a shell command to a variable. You can add your thoughts to this post via the feedback section below.
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
► Read more: http://adf.ly/1n5Z7T
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
No comments:
Post a Comment